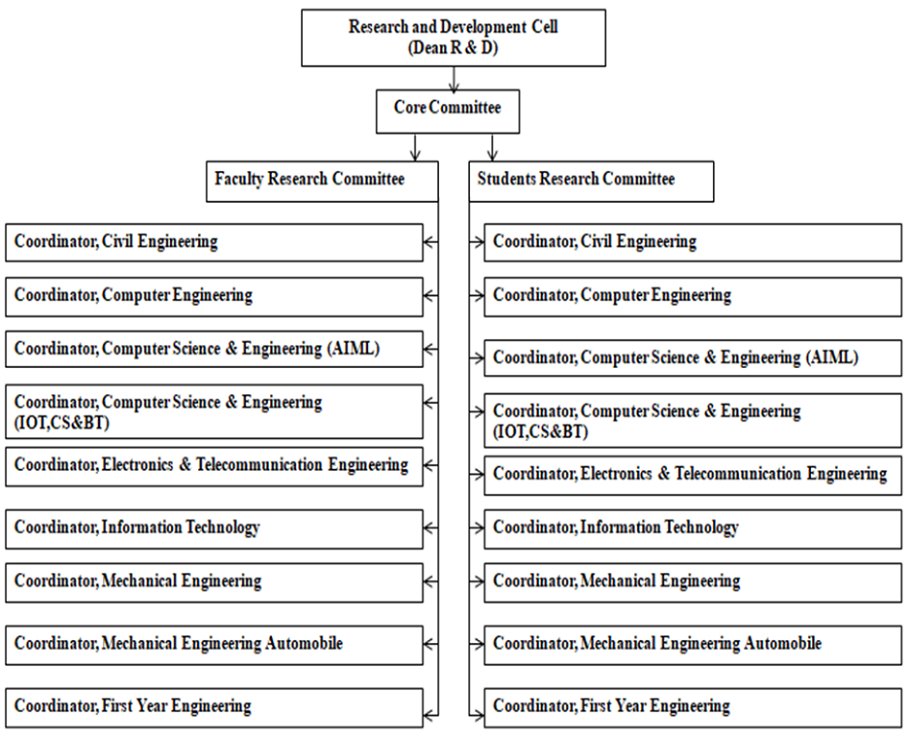
Research and Development Committee
| Sr.No | Name |
|---|---|
| 01 | Dr. Ganesh S. Kame, Chairman, Dean ( R & D) |
| 02 | Dr. Nazneen Pendhari, Member (Convener, EDC) |
| 03 | Dr. Javed Shaikh, Member (Convener, PDC) |
| 04 | Dr. Amol Sankpal, Member (Co-convener, PDC) |
| Sr.No | Name |
|---|---|
| 01 | Dr. Uma Kale, Civil Engineering |
| 02 | Dr. Nazneen Pendhari, Computer Engineering |
| 03 | Er. Chaitali Mahajan, Computer Science Engineering (AIML) |
| 04 | Er. Zafar Khan, Computer Science Engineering (IOT,CS&BT) |
| 05 | Dr. Zainab Mirza, Information Technology Engineering |
| 06 | Dr. Sha Husain S. Maghrabi, Mechanical Engineering |
| 07 | Dr. Anup Chawan, Mechanical Engineering Automobile |
| 08 | Dr. Nayana Chaskar, Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering |
| 09 | Dr. Adil Khatri, Basic Science and Humanities |
| Sr.No | Name |
|---|---|
| 01 | Sayed Hassan Fahim, Civil Engineering |
| 02 | Taibani Abdul Razzak, Civil Engineering |
| 03 | Ruzain Rar, Computer Engineering |
| 04 | Salique Khan, Computer Engineering |
| 05 | Mahek Mukadam, Computer Science Engineering (AIML) |
| 06 | Huma Farid, Computer Science Engineering (AIML) |
| 07 | Ebraheem Bambotia, Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering |
| 08 | Saad Bandarkar, Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering |
| 09 | Abubakar Shaikh, Information Technology Engineering |
| 10 | Aditya Yadav, Information Technology Engineering |
| 11 | Saniya Shaikh, Mechanical Engineering |
| 12 | Ammar Nawab, Mechanical Engineering |
| 13 | Sayyed Md.Adil Md.Salim, Computer Science Engineering (IOT,CS&BT) |
| 14 | Sayyed Nouman Riyaz Ahmed, Computer Science Engineering (IOT,CS&BT) |
List of process under R & D
Coordinator: Dr. Zainab Mirza
Introduction
This process collects all research paper details from students and faculty for reimbursement. Data collection includes information about the paper like title, conference/journal information.
Process Diagram
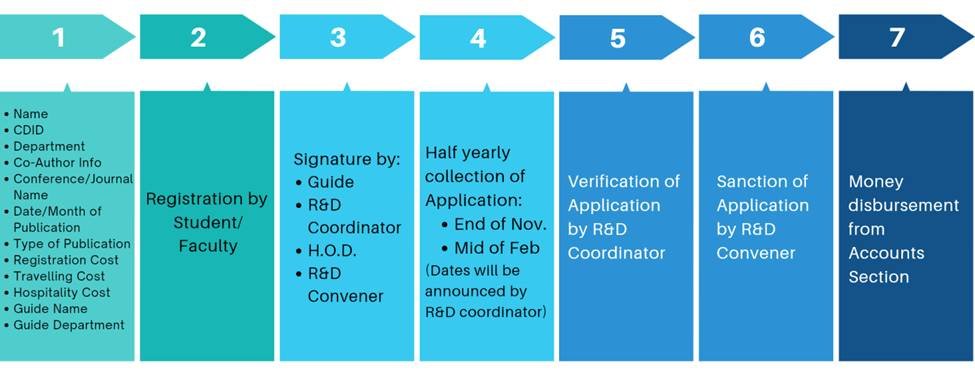
Description of Process
- Registration
- Fetch Data for the papers as per student / faculty
- Name of the Student, CDID (College Domain ID), Dept / Name of the Faculty, Dept, Designation
- Name of the Co-author (Student with their name, CDID, dept)/name of the co- author faculty (Name, dept, designation)
- Name of the guide (Dept, name)
- Title of the paper
- Name of the conference, date, hosting institute name and venue, type of conference/name of the journal, date of publication, type
- Reimbursement details like registration cost, traveling cost, stay cost(both for student/faculty)
-
Reimbursement Application
- Collected requests from faculty and students will be processed for research paper reimbursement.
- The application will be sanctioned/declined by the Admin.
Objectives
- High-Impact Publications : Support faculty and students to publish in reputed journals and conferences, improving H-Index.
- Interdisciplinary Research : Encourage impactful publications through cross- disciplinary collaboration.
- Quality Standards : Ensure rigorous review for high-quality research outputs.
Outcomes
- More Quality Publications : Growth in reputed journal and conference papers, strengthening H-Index.
- Interdisciplinary Excellence : Increased impactful interdisciplinary publications..
- Uphold Rigorous Research Quality Standards : Research outputs consistently meeting high academic and ethical standards.
Coordinator: Dr. Uma Kale
Introduction
The Project Exhibition is an annual flagship event organized by the Research and Development Cell of the institute. It serves as a platform for all the undergraduate students across all branches to present their innovative projects. The exhibition highlights the diverse technical capabilities, creative thinking, and research-oriented approach fostered within the academic environment of the institute.
Process Diagram
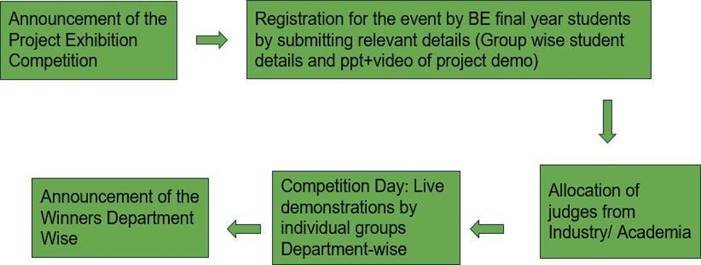
Description of Process
The exhibition involves the display and demonstration of final-year student projects from various engineering disciplines. Each participating team is allotted space to showcase their working models, prototypes, or software applications. Industry experts, faculty members, and peers are invited to evaluate the projects. The event encourages interdisciplinary collaboration, practical problem-solving, and innovation among students.
Objectives
To provide a competitive and encouraging platform for students to:
- Exhibit their technical and research work
- Demonstrate their problem-solving capabilities
- Gain confidence through interaction with evaluators and visitors
- Foster innovation and teamwork
Outcomes
After participating in the Project Exhibition, students will be able to:
- Display and explain their projects effectively
- Showcase their engineering skills and innovative thinking
- Receive constructive feedback from judges and industry professionals
- Enhance their presentation, communication, and technical documentation skills
- Get recognition and motivation for future innovation
Coordinator: Dr. Anup Chawan
Introduction
This process is for providing financial assistance to UG students for national and international
collaborative research work with other institutes. The UG student has to identify a faculty
supervisor from MHSSCOE and must work with the faculty towards completion of the research
project undertaken. RIOUES Projects should typically run for a period of at least 6-12 months.
RIOUES Process Flowchart
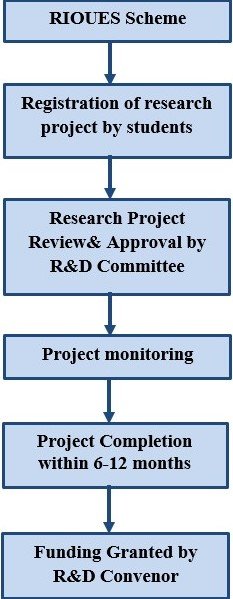
Description of Process
- Registration of research project by Students
Students should register the research proposal/project undertaken specifying the following details:- Academic year
- Department
- Student details: Roll no., Name, Email
- Project title
- Details of the collaborating institute/company
- Faculty supervisor details
- Funding required
-
Research Project Proposal review and approval
The concerned faculty supervisor and R&D committee should be able to review and approve the students’ research project proposal. -
Project Monitoring
The concerned faculty supervisor will track the research project's progress against its plan, identifying potential issues if any, and taking corrective actions to ensure the project stays on schedule, within budget finalised, and conforms to the objectives -
Funding Granted
Amount to be sanctioned for the research project to be granted by the R&D Convenor. - To give students exposure to collaborative research work.
- To enhance innovations by collaborative research.
- To expose students to apply scientific rigor and interdisciplinary approach for solving research problems.
- To increase the transfer rate of research work to practical applications.
- To give students exposure to experience diversity and equality.
- Fostering Innovation and Creativity
- Improved Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
- Enhanced Communication Skills
- Increased Knowledge and Depth of Understanding
- Development of Teamwork and Leadership Skills
- Exposure to Different Research Methodologies
Objectives
Outcomes
Coordinator: Dr. Sha Husain S. Maghrabi
Introduction
The Technical Paper Presentation is a vital academic activity designed to foster a culture of research, innovation, and knowledge dissemination among students. Rooted in our institution's vision — "To be an institute of global repute committed to the cause of nation building through technology-based education" — this initiative serves as a platform for students to explore contemporary engineering challenges, present their findings, and contribute meaningfully to the academic and professional communities.
Process Diagram
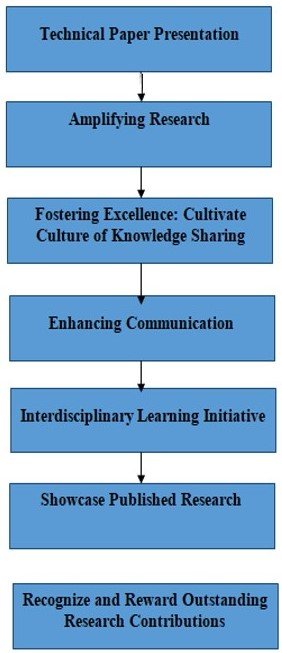
Description of Process
This process collects all research paper details from students and faculty for reimbursement. Data collection includes information about the paper like title, conference/journal information
- Registration Fetch Data for the papers as per student / faculty
- Name of the Student, CDID (College Domain ID), Dept / Name of the Faculty, Dept, Designation
- Name of the Co-author (Student with their name, CDID, dept)/name of the co- author faculty (Name, dept, designation)
- Name of the guide (Dept, name)
- Title of the paper
- Name of the conference, date, hosting institute name and venue, type of conference/name of the journal, date of publication, type
- Reimbursement details like registration cost, traveling cost, stay cost(both for student/faculty)
-
Reimbursement Application
- Collected requests will be sanctioned for research paper reimbursement by both (faculty/ student)
- Admin will be sanction/decline the application
Objectives
- To present the technical or research findings in a clear, concise, and organized manner.
- To emphasize the importance and relevance of the research or technical work, explaining how it contributes to existing knowledge or practices.
- To engage the audience through questions, discussions and encourage feedback or new ideas.
- To utilize visual aids to effectively convey complex data and concepts, making the information more accessible and easier to grasp.
- To learn the time management by delivering the presentation within the allotted time.
- To provide insights or recommendations that could guide future research, development, or practical applications based on the findings.
Outcomes
- Demonstrate an understanding of core engineering principles and theories.
- Identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems.
- Conduct research using appropriate methodologies.
- Design systems, components, or processes to meet desired needs.
- Utilize modern engineering tools and techniques.
- Understand and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities.
Coordinator: Er. Chaitali Mahajan
Introduction
The Best Research Award aims to promote a strong research culture by recognizing outstanding contributions from both faculty and students. This initiative motivates individuals to engage in high-quality research, publish in reputed journals, participate in sponsored projects, and contribute to the advancement of science, technology, and innovation. The process ensures a transparent, criterion-based evaluation to celebrate achievements and encourage a spirit of inquiry, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
Process Flow Diagram
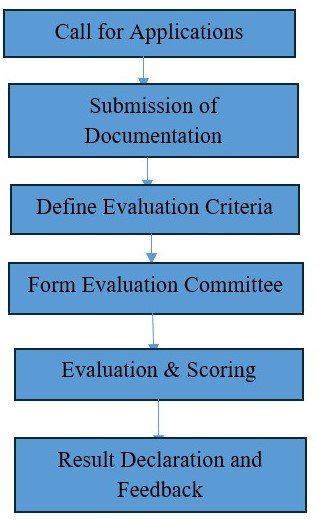
Description of Process
A call for applications (faculties and students) is issued to invite interested and eligible candidates. Applicants are required to submit all necessary documents within the specified deadline. Clear and transparent evaluation criteria are then defined to ensure a fair assessment process. An evaluation committee is formed to review the submissions. The committee evaluates each application based on the established criteria and assigns appropriate scores. Once the evaluation is complete, the final results are compiled and officially declared to all applicants.
Objectives
- To foster academic excellence by encouraging publishing in reputed journals, conferences, mentoring UG and PG research, and engaging in sponsored projects and innovation.
- Motivates ongoing contributions.
- Collaboration with industry and funding bodies creates a thriving research ecosystem that drives growth and impact.
Outcomes
- Establishment of a vibrant and dynamic research culture that inspires both faculty and students to produce high-quality, impactful research.
- Fosters an environment of academic excellence, encouraging increased publications in reputed journals, successful participation in sponsored projects, and significant advancements in science, technology, and innovation.
- It cultivates a spirit of collaboration, inquiry, and continuous improvement, ultimately contributing to the growth of a globally competitive research community within the institution.
Coordinator: Dr. Nazneen Pendhari
Introduction
The Innovation & Entrepreneurship Development Cell (IEDC/EDC) nurtures technology-driven student start-ups by identifying promising ideas, providing structured mentoring, and connecting innovators with resources across the institution and external ecosystem partners. Through guided stages—idea capture, evaluation, product mentoring, and data-driven reporting—the Cell cultivates entrepreneurial mindset, multidisciplinary collaboration, and socially responsible innovation among students and faculty mentors. A data-driven reporting layer aggregates activity by year, department, and program—tracking registrations, selection rates, mentoring participation, milestone attainment, prototype development, IP attempts, and funding interest.
Process Diagram
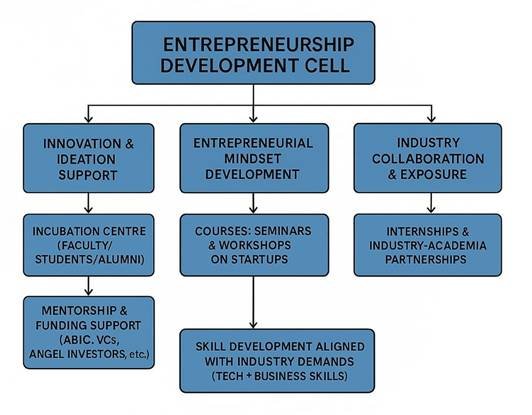
Description of Process
The flowchart illustrates the strategic framework of the Entrepreneurship Development Cell (EDC), structured around three core pillars:
- Innovation & Ideation Support
- Incubation Centre: Provides space, guidance, and infrastructure for students, faculty, and alumni to explore and test ideas.
- Mentorship & Funding: Connects teams with mentors, incubators, and investors for business planning, funding, and go-to-market strategies.
- Entrepreneurial Mindset Development
- Courses & Workshops: Sessions on startup models, pitching, and problem-solving with real-world case studies.
- Skill Development: Training in technical, business, and soft skills aligned with industry demands.
- Industry Collaboration & Exposure
- Internships & Partnerships: Engagements with startups and companies through internships, projects, and MoUs.
- Market Exposure: Builds understanding of customer needs and professional environments.
Objectives
- Encourage Entrepreneurial Thinking: Position entrepreneurship as a credible career pathway.
- Build Knowledge & Skills: Workshops on business modelling, finance, IP, product validation, and go-to-market strategy.
- Enable Networking: Access to entrepreneurs, industry experts, alumni founders, investors, and incubators.
- Support Start-Up Development: Guided ideation-to-prototype mentoring; business plan reviews; regulatory basics.
- Promote Innovation & Creativity: Apply engineering knowledge to solve real-world problems.
- Provide Incubation & Mentorship: Lab access, domain mentors, startup clinics.
- Foster Start-Up Culture: Hackathons, ideathons, pitch days, demo days.
- Build External Partnerships: Industry, government, accelerators, and academic collaborations.
Outcomes
- The learner will demonstrate entrepreneurial thinking by identifying opportunities, taking initiative, and applying innovation to create solutions or ventures.
- The learner will be able to apply essential business knowledge and skills to successfully plan, launch and manage a venture.
- Learner will be able to interact with successful entrepreneurs, industry experts, mentors and investors to gain insights and build valuable networks.
- The learner will be able to actively contribute to startup development by generating ideas, creating business plans, and navigating the legal and regulatory processes needed to launch a new venture.
Coordinator: Dr. Nayana Chaskar
Introduction
The Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) registration process typically involves filing an application, undergoing examination, publication, and ultimately, the grant of the IPR. This process varies depending on the specific type of IPR, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights. A patent provides legal protection and exclusive rights for a limited period, granting inventors the ability to control and monetize their creations. By obtaining a patent, inventors can prevent others from making, using, or selling their invention without permission.
Process Diagram
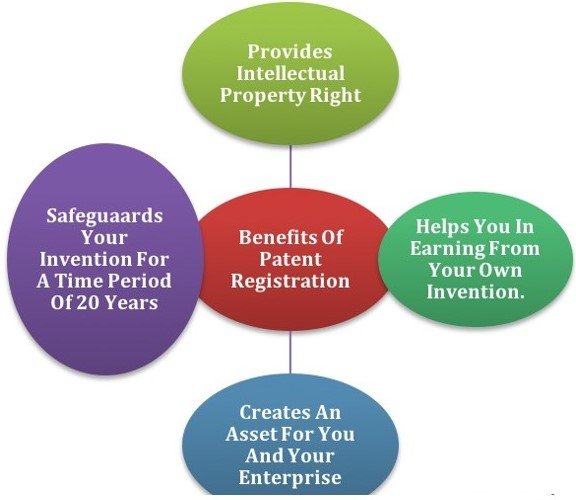
Patent registration benefits

Description of Process
Patent related information will be collected at institute level from the various departments in every academic year. The sponsored patent and non- sponsored patent information will be collected. The report will be generated to apply, grant and publish patents.
- Registration of patents from student/ faculty
- Student / Faculty Name
- Student ID/UPRN no.
- Student/Faculty Dept
- Patent Title
- Patent Domain
- All patent related data as per standard format
- Patent mentoring and performance evaluation process
- Evaluation of the patent filled data as per the standard format
- Project date completed
- Applicability of patent
- Permission to submit the patent(Yes/No)
- Application of patent
- All collected idea submitted to IPR office
- Final patent ID
- Status monitoring for patent
- Final Patent ID
- Status of patent
- Report generation
- Choose the type (year, dept, program)
- Generate excel sheet of the statistics based on (year, dept, program)
- Analyzing the data and creating visualizations for understanding the static and growth percentage compared to past data
Objectives
Maximisation of the number of patent filing in institutes every academic year with the new ideas and innovations is engineering & multidisciplinary branches, so that inventors can protect their intellectual property, gain a competitive advantage and potentially generate revenue through licensing or commercialization as well making it more attractive to investors or potential buyers.
Detailed description of the objectives -
The objective of filing a patent application is to secure legal protection to protect intellectual property rights, exclusive rights for an invention and prevention of unauthorized use.
- Exclusivity and Protection: A patent grants the inventor exclusive rights to make, use, sell, and import the invention for a limited period, typically 20 years from the filing date in India. This prevents others from exploiting the invention without permission.
- Encouraging Innovation: The patent system is designed to incentivize inventors by offering protection and potential financial benefits for their creative efforts, thus fostering research and development.
- Monetization of Invention: Patents can be valuable assets, allowing inventors to generate revenue through licensing agreements or by selling the patent rights.
- Competitive Advantage: A patented product provides a significant edge in the market as it cannot be replicated by competitors, enhancing market share and reputation.
- Legal Recognition and Credibility: A patent officially recognizes the inventor's work, boosting their credibility and attracting investors or partners interested in innovative ventures.
- Enhancing Market Value: A robust patent portfolio demonstrates a company's commitment to innovation, increasing its market value and potential for future profitability.
Outcomes
- Maximisation of the number of patent filing in institutes, essentially, filing a patent application serves to safeguard intellectual property.
- Promote innovation, and provide the inventor with a platform to commercially benefit from their invention.
Coordinator: Er. Zafar A. Khan
Introduction
Consultancy involves providing expert advice, analysis, and interpretation based on the specialized knowledge and experience of the Institute's faculty. Unlike research, consultancy focuses on applying existing knowledge to solve real-world problems without generating new knowledge. At the Engineering, Pharmacy, and Professional Institutes of Anjuman-i-Islam, consultancy is seen as a valuable extension of academic work, offering benefits such as enhanced professional development, stronger industry connections, and enriched teaching and research. Faculty members are encouraged to engage in consultancy activities that align with the Institute’s mission and do not conflict with their academic responsibilities.
Process Diagram
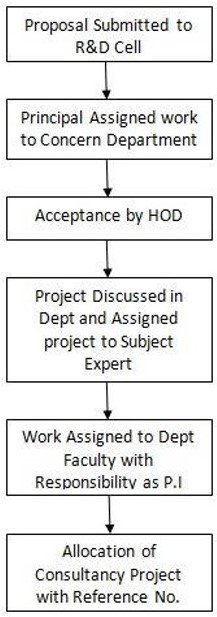
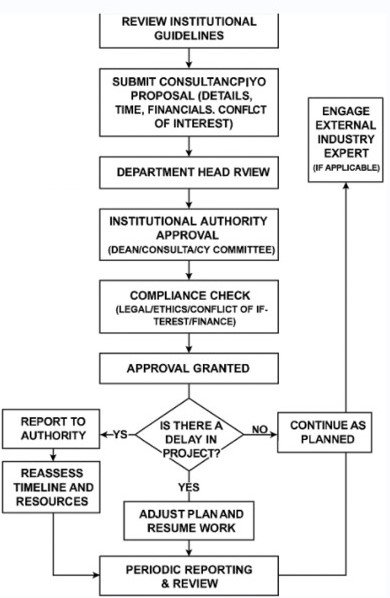
Description of Process
The consultancy work begins with a review of institutional guidelines to ensure the project aligns with established policies. A detailed proposal is then submitted, outlining aspects such as time requirements, financials, and any potential conflicts of interest. This proposal is reviewed by the department head and subsequently sent to the institutional authority—such as the dean or consultancy committee—for approval. Once the proposal clears this stage, a compliance check is conducted to address legal, ethical, financial, and conflict-of-interest concerns. After all checks are satisfied, approval is granted. If applicable, an external industry expert may be engaged to support the project. The work then proceeds as planned, with regular monitoring. If delays occur, they are reported to the appropriate authority, and the timeline and resources are reassessed. Adjustments are made to the project plan, and work resumes accordingly. Throughout the project, periodic reporting and review ensure transparency, accountability, and progress tracking.
Objectives
- Encourage faculty participation in consultancy activities that contribute to professional growth and societal impact.
- Strengthen linkages between the Institute and external organizations, including industry and government.
- Facilitate knowledge transfer and real-world problem solving through expert services.
- Ensure all consultancy engagements are conducted transparently, ethically, and with prior approval to maintain institutional integrity.
Outcomes
- Builds lasting ties with industry for mutual benefit.
- Enhances faculty and student expertise through real-world exposure.
- Boosts the college’s profile and generates additional income.
Coordinator : Er. Zafar A. Khan
Introduction
A grant is a financial award provided by a government agency, private organization, or funding body to support specific projects, research, or initiatives. Unlike loans, grants do not require repayment, making them a valuable source of funding for individuals, institutions, or organizations seeking to pursue academic, scientific, developmental, or community-based work. Grants are typically awarded based on the merit of a submitted proposal, which outlines the goals, methodology, budget, and expected outcomes of the proposed work. The grant application process often involves multiple stages of review and approval to ensure the project's alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Research Grant Application Flowchart
Research Grant Application Flowchart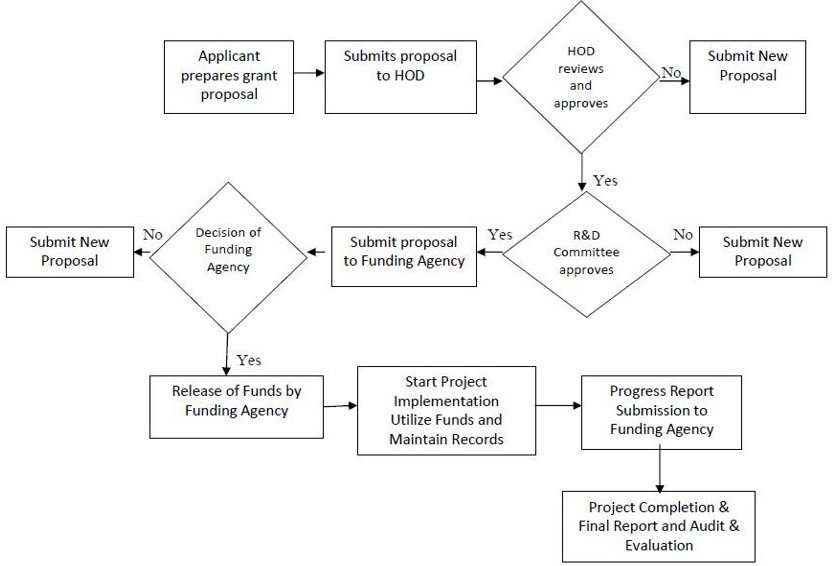
Description of Process
The flowchart outlines the brief process of applying for a grant through a structured approval system. The process begins with the applicant preparing the grant proposal. This proposal is first submitted to the Head of Department (HOD) for review. If the HOD approves it, the proposal is forwarded to the Principal for further approval. Any rejection at either stage stops the process. Once both internal approvals are secured, the proposal is submitted to the funding agency. The agency then reviews the submission and decides whether to approve the grant. If the grant is approved, the agency releases the funds, and the project proceeds to the implementation phase.
Objectives
- To secure financial support from a recognized funding agency for implementing a proposed project or research initiative.
- To ensure transparency and accountability by following a structured review and approval process involving institutional authorities like the HOD and Principal.
- To facilitate the successful execution and monitoring of the approved project through timely fund release, proper utilization, and regular reporting to the funding agency.
Outcomes
- Provides resources for advanced research, encouraging innovation and enhancing institutional reputation.
- Offers hands-on experience for students and professional growth for faculty.
- Strengthens ties with industry and funding agencies, opening doors for future collaborations.
Coordinator: Dr. Javed Habib & Dr. Amol Sankpal
Introduction
A product development cell is a dedicated unit in our organization focused on creating
and improving products. It encompasses the entire process from initial idea to market
launch, and potentially beyond, with the aim of delivering value to customers and
enhancing the company's market position. This cell brings together various specialists,
like product managers, designers, and engineers, to collaborate on product strategy,
design, development, and commercialization.
Process Diagram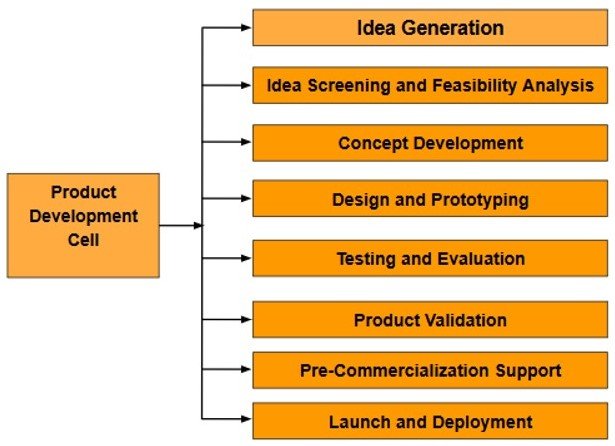
Description of Process
- Idea Generation: The process begins with brainstorming sessions aimed at generating innovative ideas. Inputs are gathered from various sources including industry challenges, student and faculty insights, and collaborations with Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). This ensures that ideas are relevant and grounded in real-world needs.
- Idea Screening & Feasibility Analysis: Once ideas are collected, they undergo rigorous screening to assess their viability. This includes technical feasibility studies, market analysis to understand potential demand, evaluation of resource availability, and a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential obstacles.
- Concept Development: Promising ideas are then transformed into concrete concepts. This stage involves creating initial design sketches, analyzing use cases, defining functional requirements, and planning prototyping strategies to bring the concept closer to reality.
- Design & Prototyping: Detailed designs are developed using CAD modeling, followed by simulation and testing to validate the design under various conditions. Prototypes are fabricated using advanced techniques such as 3D printing or CNC machining to create tangible models for further evaluation.
- Testing & Evaluation: The prototypes undergo functional testing to verify performance and reliability. User feedback is collected to identify areas of improvement, enabling iterative enhancements to refine the product.
- Product Validation: The refined product is subjected to compliance checks and reviewed by industry experts or mentors to ensure it meets required standards and expectations. Final performance assessments confirm readiness for market introduction.
- Pre-Commercialization Support: Before launch, necessary steps such as Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) filing are undertaken to protect the innovation. Business model planning and branding strategies, including packaging concepts, are developed to prepare for commercialization.
- Launch & Deployment: The product is introduced to the market through integration with MSMEs or direct market launches. Efforts include pitching to investors or incubators to secure funding and support. Post-launch activities focus on continuous support and scaling to ensure long-term success.
Objectives
- Develop students into motivated and skilled product developers through hands-on training, mentorship, and real-world project experience.
- Promote entrepreneurial thinking by encouraging student-led innovation focused on addressing local and national challenges.
- Facilitate active engagement with Micro, Small, and Medium-scale Enterprises (MSMEs) to provide students with practical exposure and collaborative opportunities.
- Support the creation of sustainable and impactful products that contribute to economic growth and social development.
- Strengthen the link between academia and industry by fostering partnerships that benefit both students and MSMEs across the country.
- Encourage student participation in national development efforts by aligning product development projects with the goals of a vibrant and sustainable economy.
Outcomes
Learners will be able to.
- Learners will be able to conceptualize, design, and develop innovative products using practical skills and mentorship.
- Learners will be able to apply entrepreneurial thinking to solve real-world problems with market-ready solutions.
- Learners will be able to gain hands-on experience by collaborating with MSMEs on real industry projects.
- Learners will be able to create sustainable, socially responsible, and economically viable product solutions.
- Learners will be able to engage in academia-industry partnerships through joint projects and internships.
- Learners will be able to contribute to national development goals through aligned and impactful innovations.
